 |
| Wake up! |
Coffee Break. 5 minutes. Back to work. Finally start to wake up ....
This would be the description of a normal working day for many, with the cycle repeated n times and substituting for some coffee or Coca-Cola energy drink or something sweet tooth for chocolate. In any case what we are doing is administered a dose of caffeine .
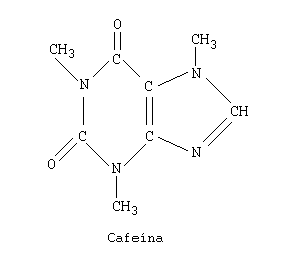 |
| This simple molecule is the culprit |
How much caffeine is too much caffeine? some would say easy: when you see your partner with wide eyes, running the lab Espido with a pulse worse than a Parkinsonian (pardon me) know who has taken one or two more cafes. In fact, there is talk that the daily dose of caffeine should not exceed 500-600mg ( Mayo Clinic) which amounts to about 5 or 6 pubs (though not all coffees have the same caffeine content, as I have seen since I arrived in Germany). It's hard to die from an overdose of caffeine, but not impossible. In fact, the United States last year a boy died at a party because they ingested caffeine powder in a dose of about 20 grams, about one hundred times the normal dose (200mg would cargadito coffee caffeine), and only 2 grams would go straight to hospital. Scicurious has more details of how one dies from an overdose of caffeine (in English) but I wanted to talk a little more than a good side.
obvious effects are to decrease fatigue and increase alertness, that is: we wake up, and improves performance on simple tasks that require attention even when the task is more complex is not so clear your contribution, so does memory has not been able to show that there are clear cognitive benefits associated with the consumption of caffeine in addition, of course, that sleep is difficult to study, to cite one example (ref. 1).
However, its effects vary from person to person, may generate anxiety, insomnia and super-sensitive in people who have certain genetic variants in the dopamine (neurotransmitter associated with the sensation of reward and pleasure) and adenosine (the receptor that also binds to the caffeine, ref. 2 ) and in all cases when one is "removed " appears as a side effect bad mood (ref . 1 ). Has also been reported that caffeine may be helpful in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (ref. 3) and Parkinson (ref. 4) as well as dementia. Epidemiological studies found an inverse correlation between caffeine intake and the incidence of Parkinson's or Alzheimer's (ie, those who drank caffeine regularly in old age often suffer less disease degenerative) and although this type of study yields mixed results sometimes, experiments in animal models appear to support the causality: that is, caffeine has a beneficial effect per se (in short, ref. 5 ).
also, and to my surprise, there are even protocols on how to get the most out of caffeine to enhance performance (ergogenic) of athletes based on the dual effect of caffeine on the nervous and muscular (ref. 6). A meta-study (comparing the results of studies published to date) on the effects of caffeine on the yield point improvements from 3mg/kg body mass but also points out the shortcomings as to what the ideals of management protocols and in what sports the greatest benefits are observed (ref. 7). However, since 2004, the caffeine is out of the black list of doping agents because caffeine in doses of 3-4mg/kg are the usual mass of the "usual" for more details I recommend the article Miguel Foundation Indurain.
So caffeine is good for students, athletes, workers on night shift, dads, moms, children (or you think that has the ColaCao), the elderly and of course the scientists! So if your first queries genotype if you want to have anxiety disorders and controls dose, there is much vice.

0 comments:
Post a Comment